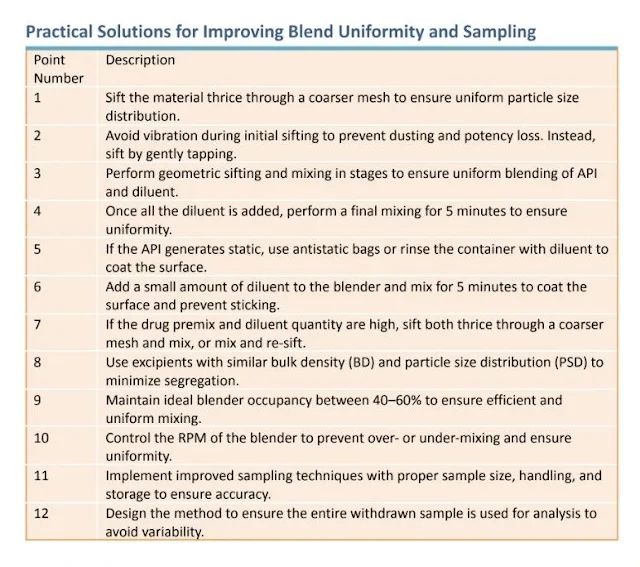
1. Sift the material thrice through a coarser mesh to ensure uniform mixing.
2. Avoid vibration during initial sifting:
- Do not use vibration in the sifter during the initial stages, especially when the drug quantity is high.
- Using vibration at this stage may cause dusting of the drug, leading to potency loss and uneven distribution.
- Instead, perform sifting by gently tapping to prevent excessive dust generation.
3. Perform geometric sifting and mixing:
- For example, if you have 1 kg of API, sift it with 2 kg of diluent thrice and mix in the blender.
- Take out the blend, then mix it with 6 kg of diluent.
- Continue this process stepwise until all the diluent is added and mixed.
4. Once all the diluent is added, perform a final mixing for 5 minutes to ensure uniformity.
5. If the API tends to generate static:
- Use antistatic bags for handling and mixing.
- Alternatively, rinse the polybag or blending container with a small amount of diluent to coat the surface.
6. Add a small amount of diluent to the blender and mix for 5 minutes to coat the blender's surface, ensuring the API does not stick to the walls.
7. If the drug premix and diluent quantity are very high:
- Sift both the premix and the diluent thrice through a coarser mesh and mix.
8. Use excipients with similar bulk density (BD) and particle size distribution (PSD):
- This minimizes segregation and ensures better blending uniformity.
9. Maintain ideal blender occupancy:
- Ensure the blender is filled to 40–60% of its capacity for efficient mixing and to avoid over- or under-blending.
10. Control the RPM of the blender:
- Optimize the blender's speed to prevent over-mixing (leading to segregation) or under-mixing (causing poor uniformity).
- Typically, a lower RPM is suitable for sensitive blends, while higher RPM may be used for less cohesive materials.
11. Improved Sampling Technique:
- Ensure the entire withdrawn sample is used for analysis to avoid variability caused by partial sampling.
- Take a correct sample size, usually X to 3X of the required amount.
- Use glass vials for sampling. If sampling on butter paper, ensure the full material is transferred into a vial.
- Keep vials upright and use a vial cage to prevent them from falling.
- Rinse vials during analysis with diluent for complete extraction.
- Perform triplicate sampling to cross-check results.
- Store samples under proper conditions to maintain integrity.
- Never collect samples on butter paper, as material may stick or fall from packets.
- Use antistatic stoppers when sampling with vials to prevent static charge effects.
12. Design the method to avoid partial sampling:
- The method should ensure that the entire sample withdrawn is used for analysis, as partial sampling can lead to variability and inaccuracies.
- Blend Uniformity Analysis
- Data-Driven Sampling Plan for Uniformity of Dosage Unit
- Differences Among Blend Uniformity, Content Uniformity and Weight Variation